In a heart-pounding rescue operation, a dedicated team of heroes faced a race against time to free Ziggy, a 10-year-old Patterdale terrier, from a perilous underground bunker. This harrowing ordeal left everyone on edge as they fought tirelessly to save a beloved pup trapped in a dire situation.

Ziggy had been enjoying a carefree day on his family’s farm, frolicking alongside his mom when an unexpected turn of events sent him spiraling into a dark abyss—an underground drain pipe. At first, his mom wasn’t overly concerned; after all, this wasn’t Ziggy’s first escapade into subterranean exploration. But as the minutes turned into hours, and Ziggy failed to reappear, panic set in.
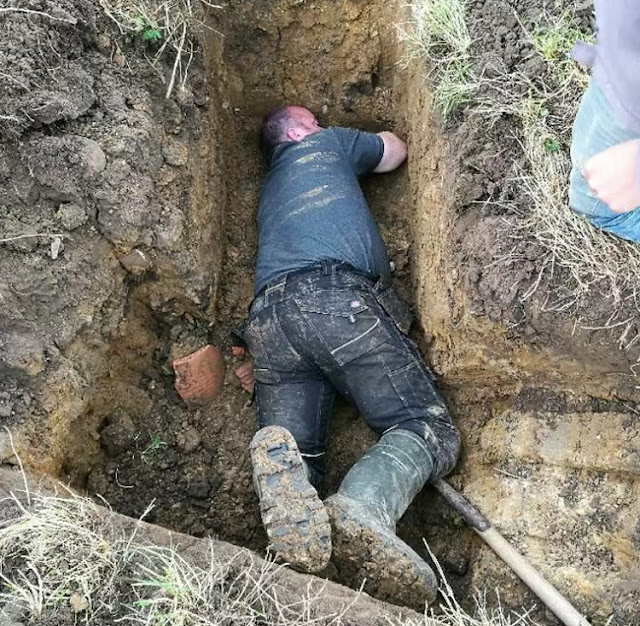

Lauren Flintoft, Ziggy’s mom, shared her worry, saying, “I was worried he might have been stuck, and that’s why he didn’t appear. My husband Tim spent the whole night trying to entice him out, and when he didn’t emerge, I called in help.”
Desperate for aid, Flintoft reached out to the RSPCA (Royal Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals) with hopes that they could assist in rescuing Ziggy from his precarious predicament. A team of dedicated rescuers promptly arrived at the scene, ready to tackle the daunting task of locating and liberating the trapped terrier.

The operation was not for the faint of heart. Rescuers had to meticulously map the complex underground pipes, meticulously plotting their course to reach Ziggy. With unwavering determination, they began to dig two enormous holes, strategically positioned to expose Ziggy’s location.
Finally, after hours of relentless effort, the group spotted a glimmer of hope—a glimpse of Ziggy’s furry form within the confined space. With great care and precision, they gently cleared away the debris that held Ziggy captive, allowing him to wiggle his way to freedom. Remarkably, Ziggy had endured an astonishing 19 hours trapped in the drain pipe.
Despite his extended ordeal, Ziggy emerged from his subterranean prison unharmed, albeit a bit shaken. He was swiftly reunited with his relieved family, basking in the warmth of their embrace. This heartwarming rescue reaffirmed the unwavering bond between humans and their faithful canine companions.

Faebian Vann, an animal collection officer with the RSPCA, joyfully shared, “He’s now back home with his owners where he belongs, and no doubt he’ll be getting up to no good again very soon.”
Ziggy’s triumphant return serves as a testament to the extraordinary efforts of a dedicated rescue team and the power of compassion in the face of adversity. His story reminds us of the enduring spirit of our four-legged friends and the lengths we’re willing to go to ensure their safety and well-being.
A lot of people had a crush on her in the 1980s, but look at her now…
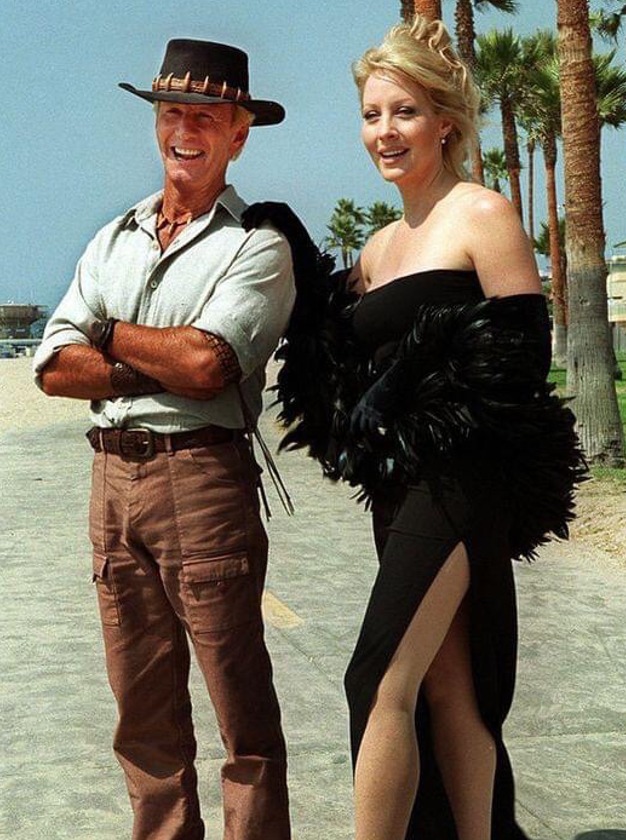

After her breakout role in “Crocodile Dundee”, Linda Kozlowski found herself thrust into the international spotlight. Starring opposite Paul Hogan, the film marked a significant milestone in her career trajectory. However, following the “Dundee” series and a handful of other projects, Kozlowski gradually veered away from the glitz and glamor of Hollywood.
Hailing from Fairfield, Connecticut, Linda Kozlowski was born on January 7, 1958, with aspirations of treading the boards. She pursued her passion for acting by enrolling in the prestigious theater program at the Juilliard School. Upon graduating in 1981, she made her mark in various off-Broadway productions before transitioning to minor roles on Broadway and television. Notably, she starred alongside Dustin Hoffman in the television movie “Death of a Salesman”, marking a significant milestone in her career.

Linda’s path to fame wasn’t without its hurdles. Following her stint as a waitress post-“Death of a Salesman”, she relocated to California. It was there, under the wing of her mentor Dustin Hoffman and his wife, that Linda found refuge in their Malibu beach house. It was from this humble abode that Linda embarked on an audition that would alter the course of her life.

Dustin Hoffman’s endorsement landed Linda the coveted role of Sue Charlton in “Crocodile Dundee”, a character she portrayed with aplomb. The film’s astronomical success, raking in over $320 million against a $10 million budget, catapulted Linda Kozlowski into stardom virtually overnight. Interestingly, her fame initially soared in Australia due to the film’s early release there.

Despite her newfound celebrity status, Linda felt somewhat overlooked in Hollywood. While she reprised her role in the “Crocodile Dundee” sequels, she declined numerous offers for roles that pigeonholed her as the quintessential girlfriend of a comedic lead. Ultimately, Linda decided to bid adieu to acting after the third installment of “Dundee”.

In her personal life, Linda Kozlowski found love on set with her co-star Paul Hogan during the “Crocodile Dundee” series. They tied the knot in 1990 and welcomed their son, Chance, in 1998. However, their marriage dissolved in 2014. Following her divorce from Paul Hogan, Linda received a substantial settlement, empowering her to chart her own course. She turned her gaze towards Morocco, where she crossed paths with Moulay Hafid Baba, a native tour guide, sparking a profound life transformation.

Together, Linda and Moulay Hafid Baba founded the luxury travel agency Dream My Destiny in Marrakech. Crafting bespoke travel experiences tailored to their clients’ desires became their passion. Linda seamlessly transitioned from the glitz of Hollywood to the enchanting vistas of Morocco.
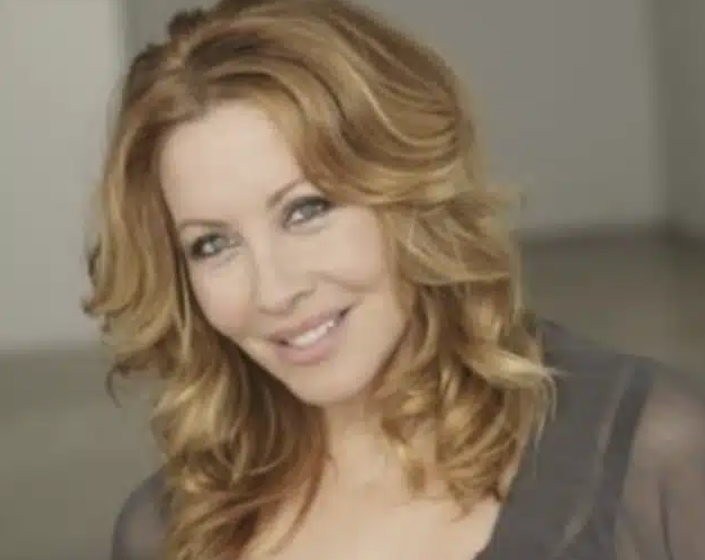

While Linda Kozlowski may have bid farewell to the silver screen, her legacy as Sue Charlton in “Crocodile Dundee” endures. At 63, she embraces her adventurous spirit and finds fulfillment in her new life in Morocco. She believes that reality surpasses fiction, channeling her intuition honed during her acting career into curating unforgettable experiences for travelers around the globe.


Leave a Reply